Step 6. Screen for the His+ Mut+ transformants
P.pastoris GS115 transformants are plated on MD (Minimal Dextrose) plates after electroporation. Incubate the plates at 30℃ for 2 days or longer. MD plate contains no histidine, thus can select out strains containing His+. Normally transformants with the phenotype of His+ Mut+ can generate single colonies within three days (Figure 1).
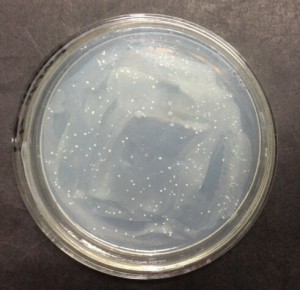
Figure 1. Transformants with the phenotype of His+ Mut+ generate single colonies on MD after incubation for two days
Antibiotic resistance genes in the backbone of expression vectors confer resistance to antibiotic in Pichia pastoris. Strains carry the backbone of pPIC9K and pPICZα are resistant to G418 and Zeocin respectively.The copy number of transformed DNA integrated into the genome of Pichia pastoris ranges randomly from one to multiple. Generally, strains with more copies of integrated DNA have higher enzyme activity as well as higher resistance to antibiotic.
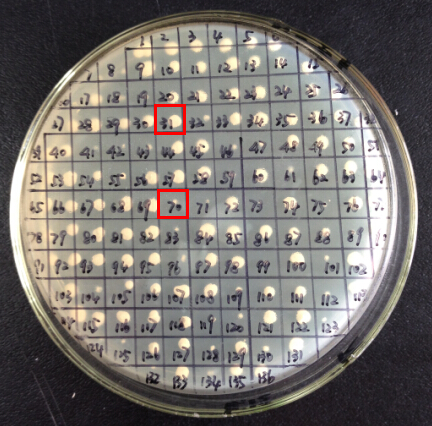
To screen for strains with high enzyme activity, we use sterile toothpicks to patch 200 His+ Mut+ transformants of each kind on new plates (Figure 2). New plates contain medium concentration of antibiotics and are free from selective pressure of lacking histidine. Media and antibiotics are chosen according to the type of plasmid backbone the P.pastoris strains carry. Strains carry pPIC9K backbone are patched on YPD plate containing 2mg/mL G418; strains carry pPICZα are patched on YPDS plate containing 200ug/mL Zeocin. Incubate the plates at 30℃ for 2 days or longer. Transformants with relatively high copy number of transformed DNA yield large circular colonies (e.g. colony 31 in figure 2), while others remain small dots (e.g. colony 70 in figure 2).
Step 7. Screen for transformants with high enzyme activity
It’s laborious and time consuming to do fermentation and enzyme activity assay, so further screenings are required to screen for transformants with high enzyme activity.
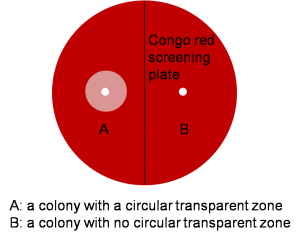
Transformants obtained after resistance selection are patched on new BMMY (medium for fermentation) plates containing substrate to corresponding enzyme; we use xylan (birchwood), common substrate of all the four cellulases we are studying. Xylose is the decomposition product of xylan. Xylan can be stained by Congo red, a dye, while xylose can’t. Congo red is added into the medium with the terminal concentration of 5mg/100mL. If the strain expresses functional cellulase, the colony will yield a circular transparent zone around (Figure 3). The strain expresses cellulase with higher activity yields transparent zone with larger diameter.
Patched Congo red screening plates are incubated at 30℃. The expression of cellulase is under the regulation of inducible promoter, PAOX1. 200uL methanol is added to the plate everyday to induce the expression of cellulase.
Unfortunately, none of our transformants yield any transparent zone after five days of induction and incubation (Figure 4); however, it doesn’t necessarily mean our transformants can’t express functional cellulase. There are many possible reasons for the failure of yielding transparent zones: 1) cellulases have many possible substrates, while xylan is not the most suitable one; 2) methanol is not the only carbon source in our BMMY medium. Other carbon sources are used prior to methanol by P.pastoris GS115, which prevents the transformants from being induced. 3) The activity of cellulases expressed by our transformants is below the threshold of the transparent zone method.
Composition of media used in our project
MD: 1.34 % YNB, 4×10−5 % biotin, 2 % dextrose, and 1.5 % agar
YPD: 1 % yeast extract, 2 % peptone, and 2 % glucose
YPDS: 1 % yeast extract, 2 % peptone, 2 % glucose, and 1M sorbitol
BMGY/BMMY: 1 % yeast extract, 2 % peptone, 100 mM potassium phosphate, pH 6.0, 1.34 % yeast nitrogen base [YNB], 4×10−5 % biotin, and 1 % glycerol or 0.5 % methanol